Mapping Gulf currents
Deepwater Horizon, 2010
Principle Investigator: Breck Owens
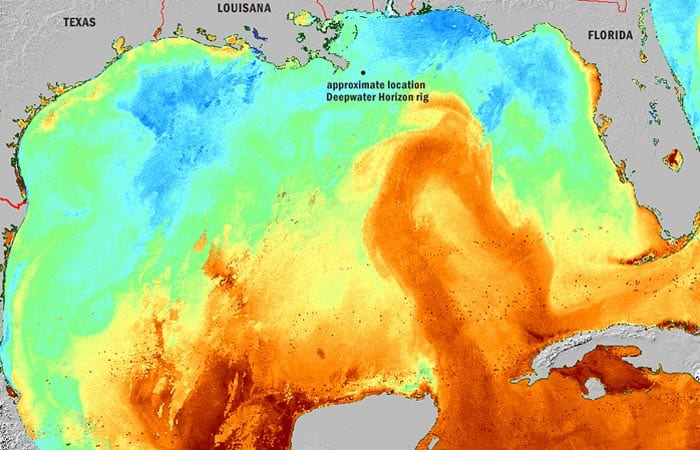
In the weeks after the Gulf oil spill started, WHOI scientists and their colleagues deployed an autonomous underwater vehicle called a Spray glider to map currents in the Gulf of Mexico from June to August. These measurements helped predict the spread of the oil at and beneath the surface and to alleviate fears that the oil would spread far beyond the Gulf.
The Loop Current is a meandering long tongue of warm water that flows from the Caribbean Sea into the Gulf of Mexico before doubling back and then veering east through the Florida Straits and joining the Gulf Stream. It has many well-known effects, from contributing to the strength of hurricanes passing over the Gulf to occasionally disrupting oil and gas drilling operations. One of the concerns during the spring and summer of 2010 was that the Loop Current could potentially carry oil out of the Gulf, up the East Coast, and out into the Atlantic.
However, with the Spray glider and other instruments in the water and transmitting data back to shore several times per day, scientists were able to watch as the Loop Current did one of its occasional switching acts. Three or four times per year, the current pinches off at its base and flows lowing directly from the Caribbean Sea to the Florida Straits while spawning a swirling eddy that slowly drifts east towards Texas.
From Oceanus Magazine
March 23, 2011
Gliders Tracked Potential for Oil to Reach the East Coast
In the early days of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, scientists and officials feared that oil could be transported through the Straits of Florida and up the East Coast. The scenario was entirely possible.
Source: Oceanus Magazine
March 24, 2005
A Glide Across the Gulf Stream
The remote-controlled Spray glider takes historic steps toward a new era of ocean exploration
Source: Oceanus Magazine
Related Multimedia
Science in a Time of Crisis, Chapter 5:Tracking the Currents
WHOI's Response to the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill
Related Technology
Spray Glider
An autonomous ocean developed at WHOI that moves through the water without external propulsion and used to track currents in the Gulf.