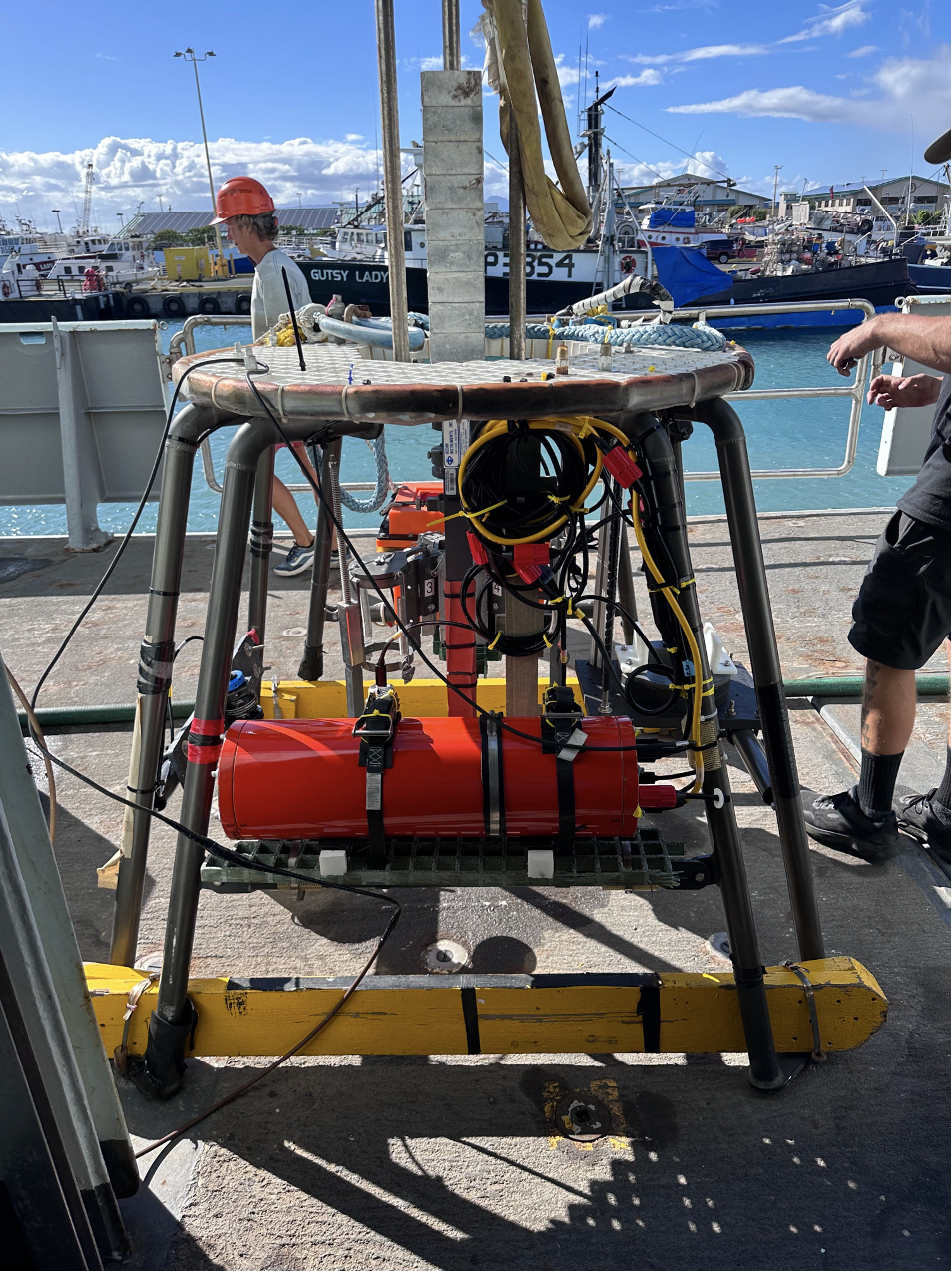
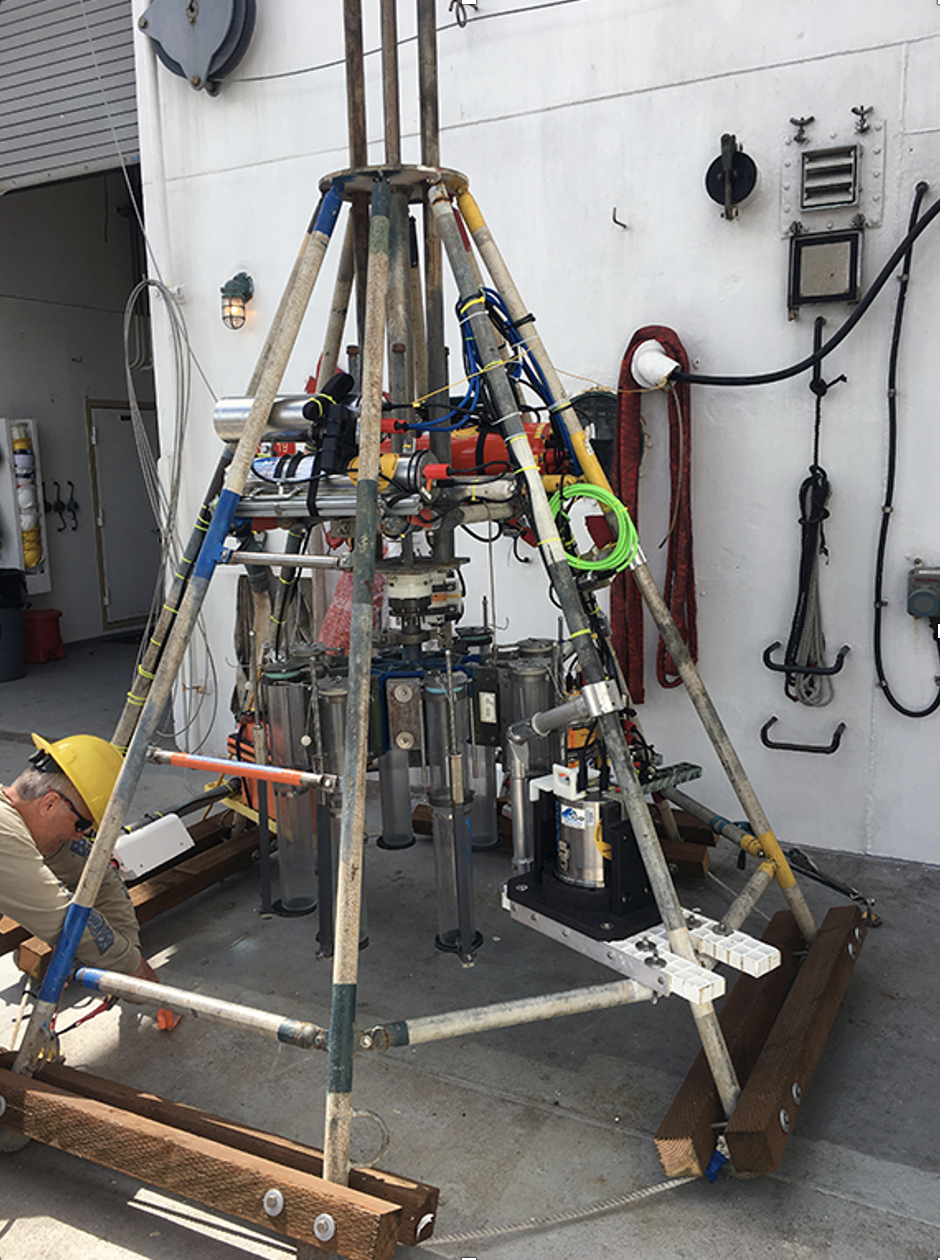
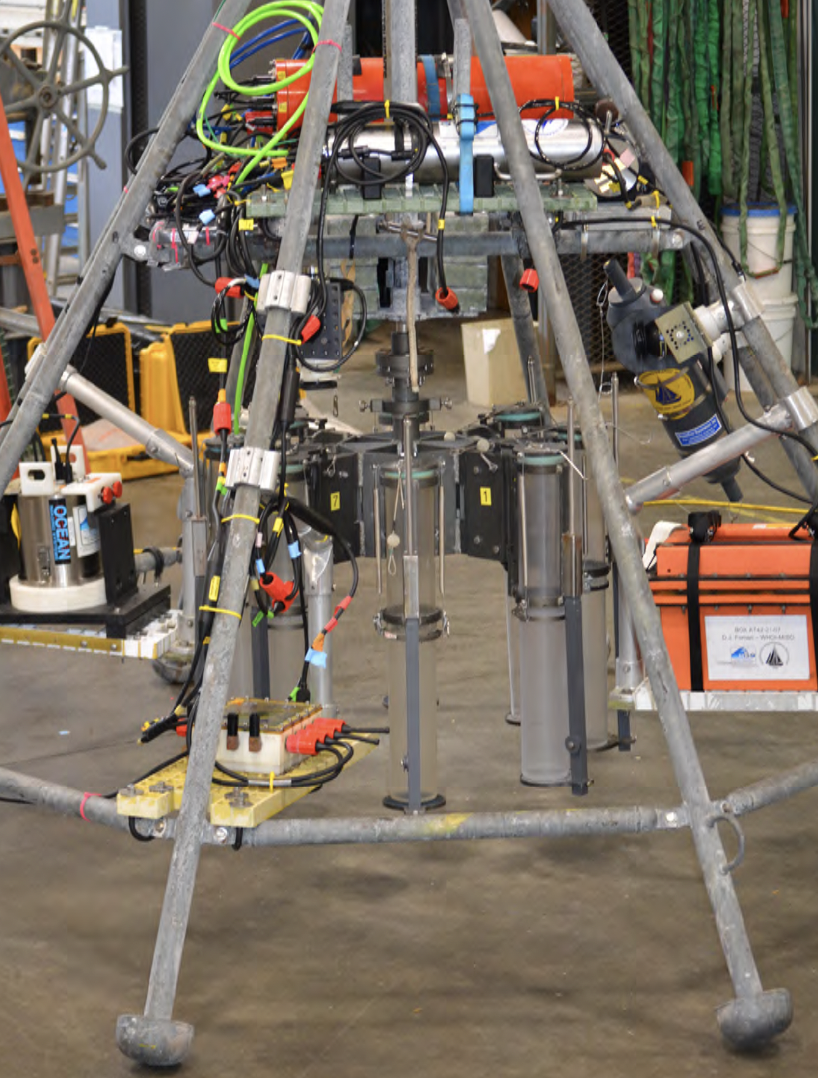
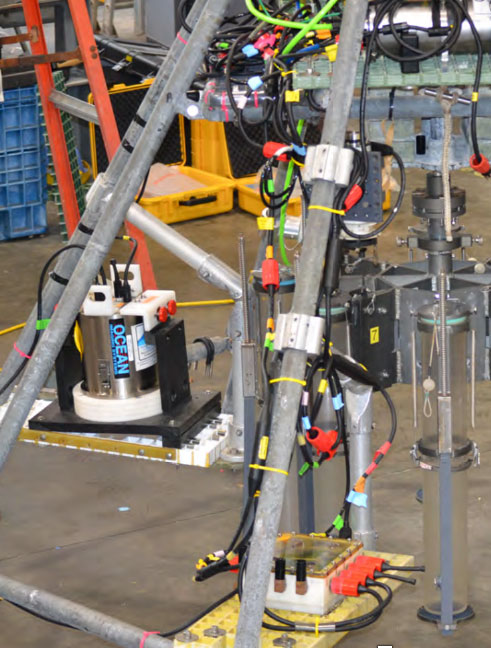
MC800 and MC400 Multi-corers with MISO Real-time Imaging and Data Telemetry
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution's Multidisciplinary Instrumentation in Support of Oceanography (WHOI MISO) Facility's real-time imaging and data capabilities have been integrated with MC-800 and MC-400 multi-corers. These systems have been used successfully on numerous academic research vessels (ARVs) for science data acquisition over the last decade. Research vessels that have supported these operations include: RV Sikuliaq, RV Thompson, RV Sally Ride, RV Oceanus, RV Sproul, RV Savannah, RV Melville, RV Atlantis, RV Armstrong, , RV Helmer Hanssen, and RV Kilo Moana.
The MISO imaging and data sensors used on multi-corers can provide the following real-time capabilities to optimize sediment sampling as well as confirm the suitability of the seafloor site for sediment collection or to target specific environments for coring (e.g., seep sites). MISO instrumentation and data types that can be configured to specific science and sample acquisition objectives include:
- depth and altitude via VA500P altimeter/depth sensor recorded at 1 Hz (1/sec) for the multi-corer to ensure proper bottom landing, data are displayed in real-time and recorded to hourly files
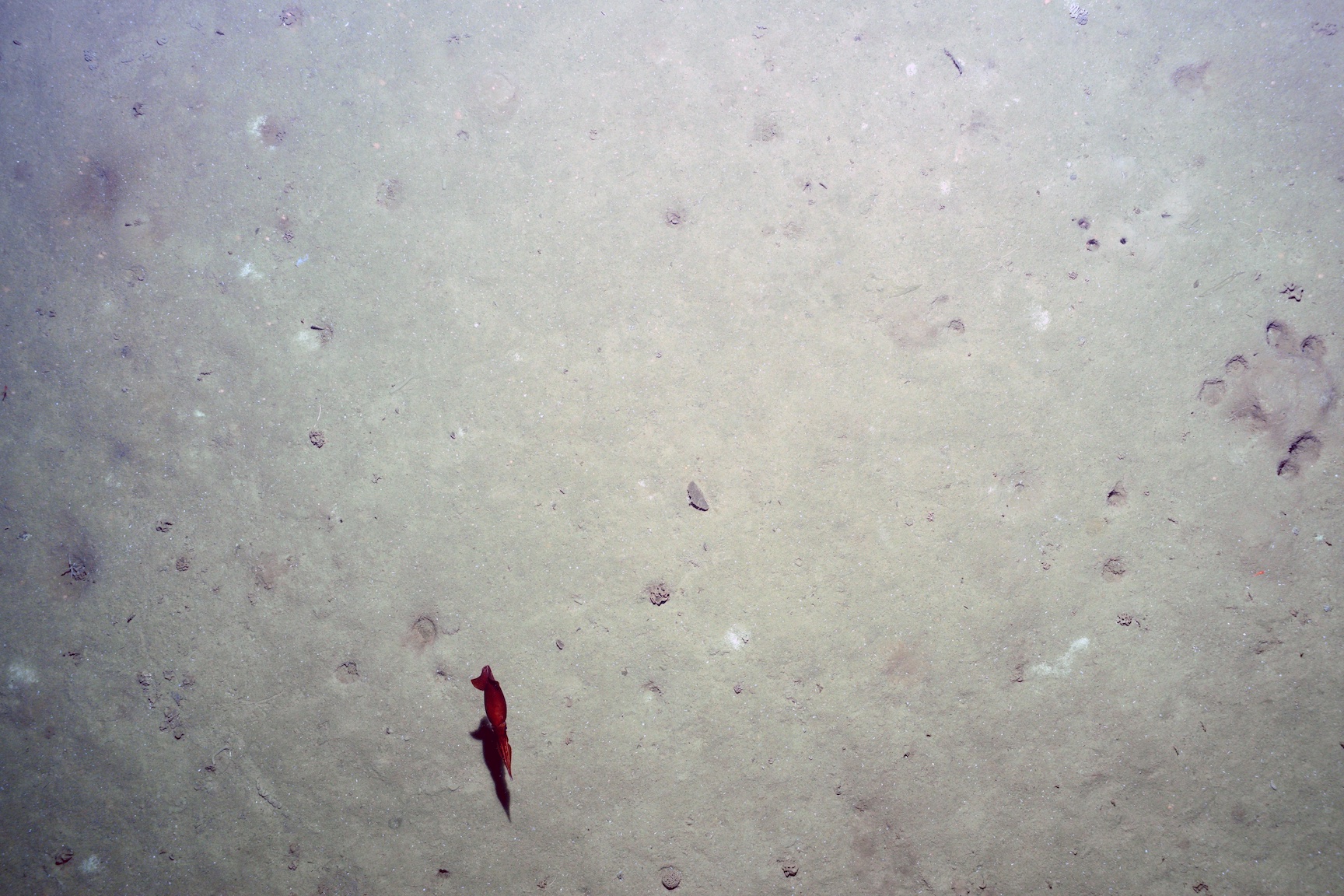
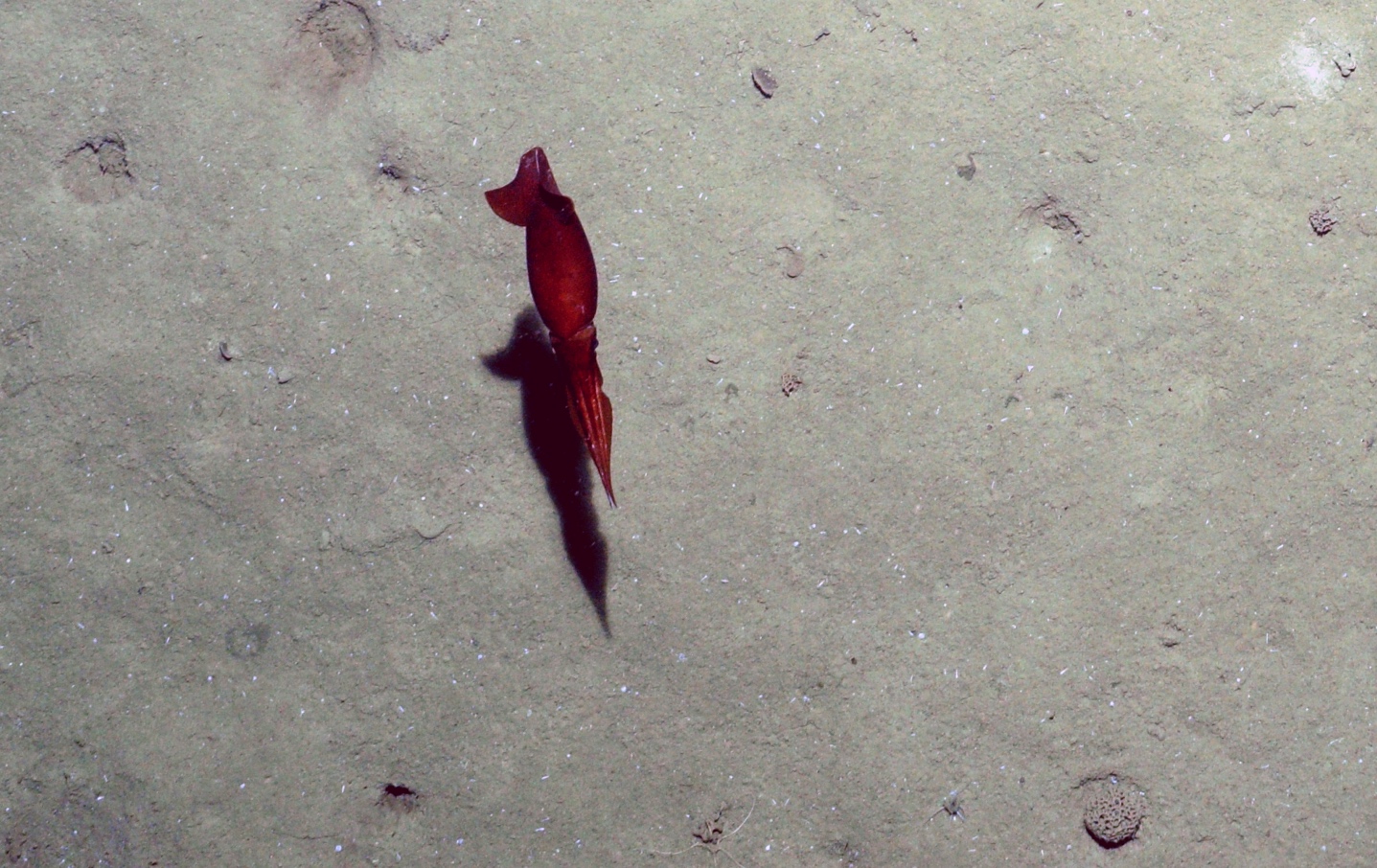
- real-time 23MP still imagery via digital-still camera every 7-10 sec with 300 watt/s strobe illumination to ensure suitability of the site for landing
- real-time analog video via deep sea video camera coupled to subsea LED lights that can be turned on/off using a software switch in the MISO 'TowCam' application that displays depth/altitude
- high-resolution (1080P to 5.3k cinematic) video recorded internally at 30 fps using MISO GoPro cameras coupled to subsea LED lighting for continuous imaging and confirmation of corer functionality and sample acquisition conditions
- water sampling near-bottom using 5L Niskin bottles triggered mechanically when the cores penetrate the seafloor
- CTD data including dissolved O2 and other basic water properties
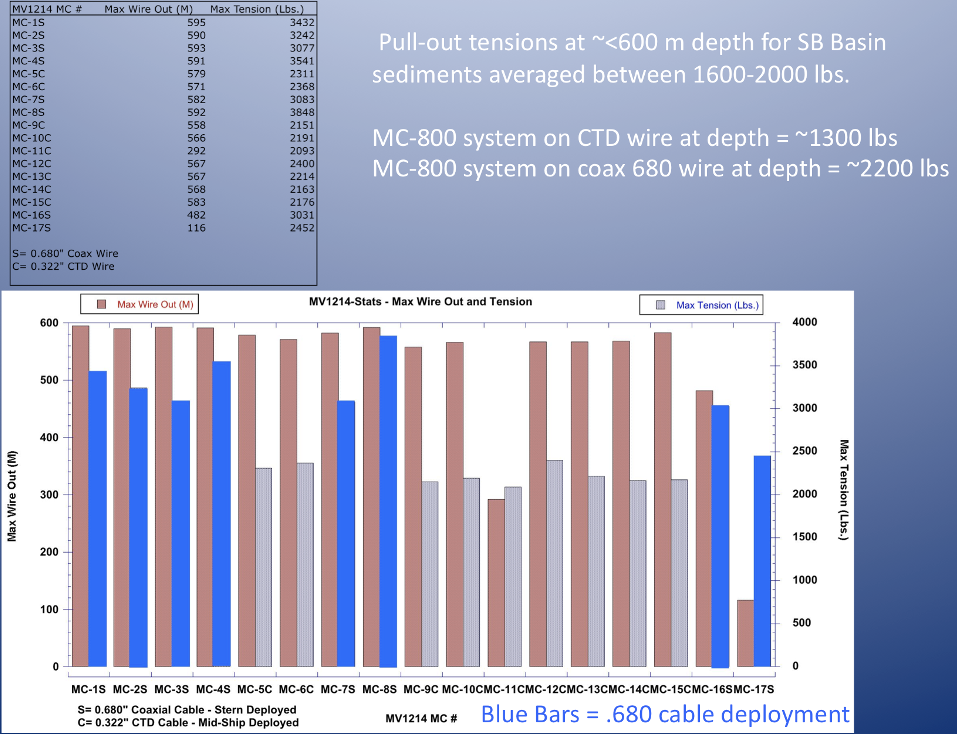
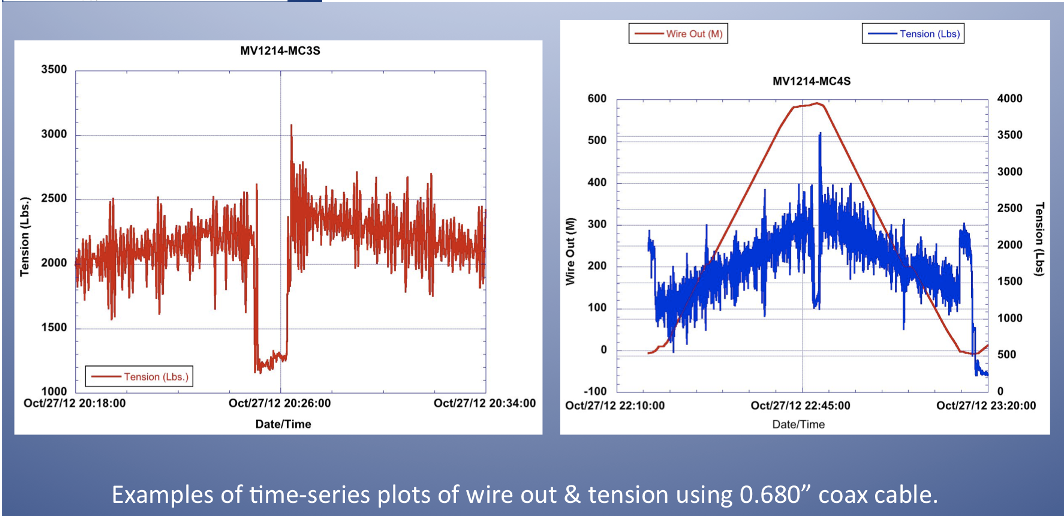
When using MISO imaging and data systems on multi-corers, the corers are tethered using a conducting cable, either 0.322” CTD, 0.680” coax, or 0.681 fiber-optic. This configuration permits the MISO DataLink telemetry system to provide real-time monitoring of the imagery and data via network extending technology implemented for MISO by H.M. Swartz (WHOI). Power for all MISO systems is provided by sealed, oil-compensated Pb-acid batteries (24 VDC) mounted on the corer frame so that only signal is transmitted up the conducting cable (2 conductors, non-polarized). No power is transmitted up the cable. Operations to ~3,500 m depth is possible using the 0.322" CTD conducting cable with a MC400, or to ~1,500 m depth using a MC800. Multi-core operations with MISO systems using either 0.680" coax or 0.681" fiber optic cable is possible to 6,000 m depth (the maximum operating depth of all MISO equipment and pressure housings).
Multi-corers - Descriptions from OSU-MARSSAM website - (P. Walcazk)
Multi corers consist of a drive carriage (spyder) that has mounting positions for multiple coring tubes. The spyder is supported by a frame that lands on the seabed, and when the wire slacks the corer slides into the sediment driven by a weight stack mounted on top of the spyder framework. When properly landed, the motion of the core tubes into the sediment is controlled and limited such that the sediment-water interface is preserved in the coring tubes, above a sediment sample that is up to ~60 cm in length. The corer can be rigged to hold an even number of tubes; up to 4 for the MC-400, and up to 8 for the MC-800.
The multi-corer provides redundant opportunities for collection of large volume samples from equivalent sediments that can be used for a variety of analyses, both shipboard and shore-based, as well as for archival of one or more complete undisturbed cores. It is an excellent option for recovering the uppermost sediment column and bottom-water interface in a wide range of lithologies, although it doesn’t work well in very sandy sediment. The polycarbonate tubes are ~80 cm in length and ~9 cm in diameter, and are fully removable for processing and archiving. MARSSAM provides skilled technical support for multi-corer operations and all expendable supplies (e.g., tubes, extruders when desired, racks for handling core tubes, etc.) and related equipment for seagoing operations involving multi-corers.
Multi-coring operations - general information
Multi-core sampling is best carried out in relatively flat seafloor environments (based on multibeam bathymetry) that have >3-5 m of sediment (based on sub-bottom profiling). Multi-corers are normally lowered at a rate of ~25-30m/min (when deeper than ~500 m) and depending on weather/sea state, and raised at a rate of ~40-45m/min once cores are collected. Upon approaching the seafloor, descent rate is decreased with altitude monitored at 1Hz using a VA500P altimeter/depth sensor so precise positioning of the multicorer is possible to help collect undisturbed sediment/bottom water inface cores. Optimal altitude for imaging the seafloor is ~4 m. Hovering over a potential sample site for 5-15 min allows for real-time confirmation of suitability of the bottom to collect good cores using the visual imagery from the still camera or video camera on the corer. After confirming that the bottom type is what the science team wants to sample, the multicore is raised to ~30 m above the seafloor, and then lowered into the sediment at ~15m/min speed, allowing for the weight of the coring rig to slowly push the four multicores into the sediment. Because of the precision of bottom contact, only 2-3 m extra wire need to be paid-out to keep the corer in the sediment and to allow the cores to penetrate (this may be weather dependent). After 4-5 minutes on bottom, the multi-corer is hauled in triggering the sealing arms and spring-loaded top to swing down and close the top and bottom of each multicore tube. The multi-corer is then hauled back to the surface and recovered on deck.
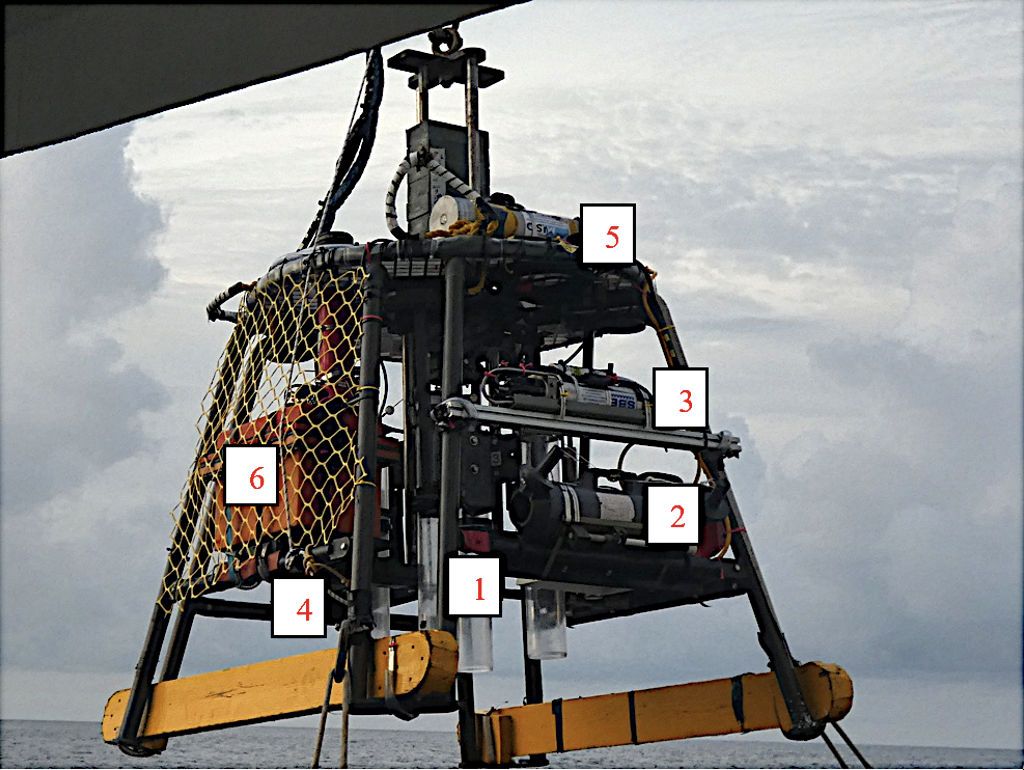
Images of a MC800 multi-corer configured with several MISO imaging and data sensors.