Uncovering climate-driven impacts on high-latitude aquifer-ocean exchange
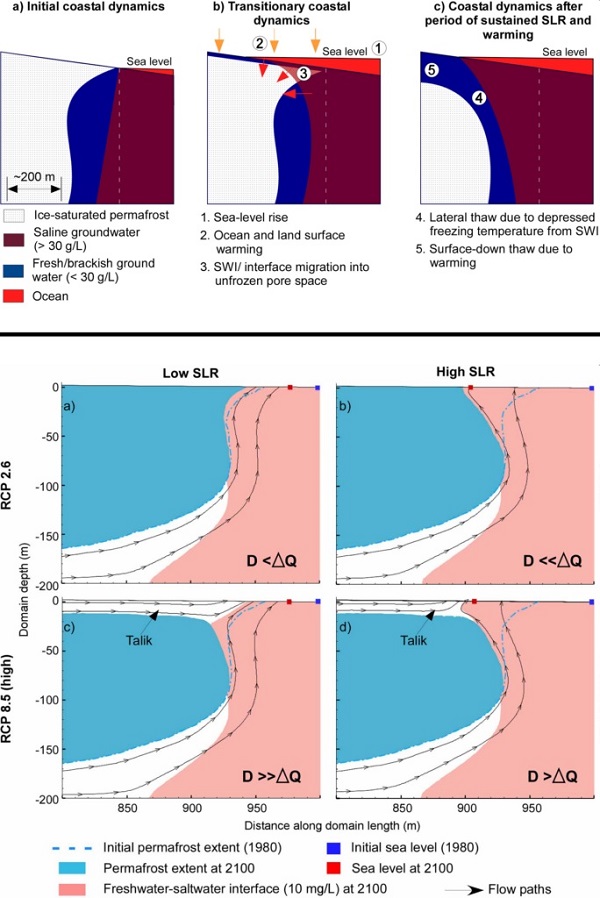 In the Arctic and subarctic, hydrogeological processes are rapidly changing due to accelerated climate change. Coastal systems are particularly vulnerable to climate-induced change due to added boundary condition changes (e.g., sea level and sea ice). The objective of this study is to investigate the impacts of sea-level rise and land surface warming on coastal permafrost extent and land-sea water exchange. This will be accomplished through the development of new process-based models.
In the Arctic and subarctic, hydrogeological processes are rapidly changing due to accelerated climate change. Coastal systems are particularly vulnerable to climate-induced change due to added boundary condition changes (e.g., sea level and sea ice). The objective of this study is to investigate the impacts of sea-level rise and land surface warming on coastal permafrost extent and land-sea water exchange. This will be accomplished through the development of new process-based models.
Software: FlexPDE
Citations: Guimond, J. A., Mohammed, A. A., Walvoord, M. A., Bense, V. F., & Kurylyk, B. L. (2022). Sea-level rise and warming mediate coastal groundwater discharge in the Arctic. Environmental Research Letters, 17(4), 045027. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ac6085
Guimond, J. A., Mohammed, A. A., Walvoord, M. A., Bense, V. F., & Kurylyk, B. L. (2021). Saltwater intrusion intensifies coastal permafrost thaw. Geophysical Research Letters, 48, e2021GL094776. https://doi. org/10.1029/2021GL094776