Developing transfection protocols and genetic tools for marine protists
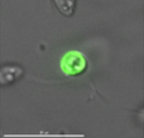
Marine protist taxa with sequenced genomes reveal that microeukaryotes can have complex and large genomes that can be many times greater in size than even the human genome. The function of a significant portion of those genes remains unknown, and has been referred to as “genetic dark matter” to reflect the fact that we know little about the role of many/most putative genes. In addition, it is unclear the extent to which many known genes play a role in interactions between marine protists and other eukaryotic and prokaryotic taxa in the marine realm, as well as in the responses of marine protists to environmental change. Our interpretation of 'omics' data from marine ecosystems is hampered by the fact that we are basing interpretations on data from only a few genetically tractable model organisms. The Moore Foundation generously provided funding to jump start the development of a wider collection of marine model protist taxa. In collaboration with the Girguis laboratory at Harvard and the Buie laboratory at MIT, we established optimal transfection protocols for a marine bodonid. We performed extensive comparisons of the efficacy of two standard cuvette-based electroporation approaches; a square wave electroporation system and an exponential decay system, and a novel microfluidics system (developed at MIT - C. Buie and P. Garcia) for transforming microbial cells developed in the Buie laboratory. The microfluidics system and its flow-through capabilities hold great promise for downstream high-throughput applications with culture collections, for testing a wide range of electroporation conditions in a single run, as as well as for working with environmental samples. Those team members included Fatma Gomaa (WHOI/Harvard), Paulo Garcia (MIT), Jenny Delaney (Harvard), Peter Girguis (Harvard) and Cullen Buie (MIT). Our target protists were successfully transfected with commercially-available plasmids.
In a subsequent project with Roberto Docampo's group (Zhuhong Li, Noelia Lander and Miguel Chiurillo) at University of Georgia, Peter Girguis and Fatma Gomaa at Harvard, and Cullen Buie at MIT, we applied custom plasmids carrying selection markers and genes of interest and have successfully achieved transient transfection using these plasmids in Bodo saltans. We successfully applied CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing in collaboration with Roberto Docampo (University of Georgia), and Mark Carrington (Cambridge, UK) to Bodo saltans.
With additional funding from the Moore Foundation V. Edgcomb, D. Beaudoin, M. Pachiadaki and F. Gomaa are collaborating with R. Beinart and J. Rotterova at URI to develop new transfection tools and to apply CRISPR/Cas9 methods to a marine ciliate that lives in anoxic sediments and hosts symbionts. New genetic tools will be used to better understand the role of symbionts in adaptation of the host to anoxia.
Protocols deposited to protocols.io include:
- G418 Kill curve protocol for selecting transfected saltans cells (dx.doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.sh4eb8w)
- - Bodo saltans culture protocol (doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.sh6eb9e)
- Generating Stable Transfection in Bodo saltans using 18s-GFP cassette (doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.s6cehaw)
- Bodo saltans Cassette for tagging EF1alpha gene__IG BsTub (doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.s5jeg4n)
- Bodo saltans tagging plasmid: 69 kDa paraflagellar rod protein 2C cassette for C terminal tagging_BsTub (doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.s5peg5n)
- Using FACS to sort fluorescent Bodo saltans cells https://www.protocols.io/view/using-facs-to-sort-fluorescent-bodo-cells-skpecvn
- Identifying an active promoter in saltans using Luciferase assay (dx.doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.shzeb76)
- Luciferase Plasmid prep (https://www.protocols.io/view/untitled-protocol-niadcae)
- Modified protocol for culturing Bodo saltans (Zhuhong Li)https://www.protocols.io/view/modified-protocol-to-improve-bodo-saltans-yield-in-9vyh67w
- Protocol for sgRNA in vitro transcription and screening for effective SaCas9 RNP complex cleavage assay dx.doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.bxbvpin6
- SaCas9 protein purification, dx.doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.bxbupinw”