Blue Carbon and the Seagrass Carbon Pump in Siliciclastic and Carbonate Sediments
This project will develop a quantitative understanding of the factors controlling carbon cycling in seagrass meadows that will improve our ability to quantify their potential as blue (ocean) carbon sinks and predict their future response to climate change, including sea level rise, ocean warming and ocean acidification. The research will advance a new generation of bio-optical-geochemical models and tools (ECHOES) that have the potential to be transform our ability to measure and predict carbon dynamics in shallow water systems. The award will also be used to train the next generation of young scientists by supporting the research of an early career scientist, two Ph.D. students, at least 2 undergraduate students, and at least two interns from the Ocean Lakes High School (Va. Beach) Math & Science Academy, under the combined supervision of the PIs. All students will participate in experimental design, implementation and data analysis and will present the findings of their research at major international scientific meetings each year as well as publishing their results in top-ranked peer reviewed journals. PI Zimmerman maintains an ongoing outreach collaboration with the Virginia Aquarium & Marine Science Center to facilitate the development of educational interpretation and programming from this project that will be specifically targeted to the >700,000 Aquarium visitors annually. The physical setting of the Aquarium will be used as a forum to engage the visitors in dialogue about the broader issue of climate change with Aquarium staff and volunteers. Zimmerman is collaborating with the Virginia Aquarium to help design and implement additional educational programs, resources, and exhibits including the development a new Chesapeake Bay tank that will house living seagrasses. The results from this project will be incorporated into Virginia Aquariums year-long Mentoring Young Scientists program and as standards-based educational materials for use at the Aquarium in programs for schools, scouts and general audiences. At various times throughout project, the PIs and students will participate in the Virginia Aquariums Speaking of Science lecture series, which are free to general public to help connect our research with the local community.
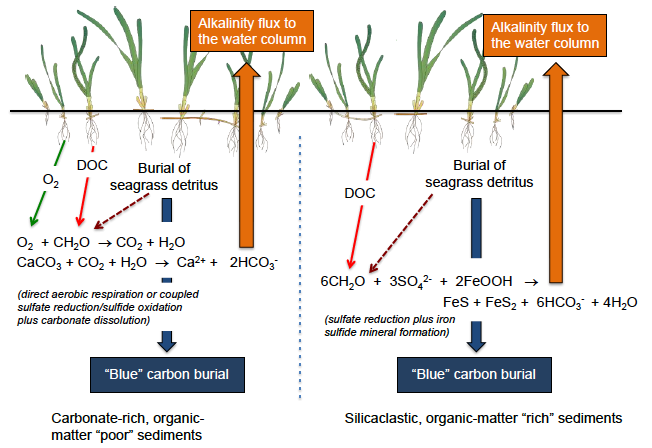
Figure 2. Conceptual diagram of the Seagrass Carbon Pump (blue carbon burial + alkalinity flux) linking the production/burial of organic matter (DOC and POC) and below-ground transport of O2 by seagrass to biogeochemical processes in the sediment that remineralize organic matter and generate alkalinity available to the overlying water column. In siliciclastic sediments, below-ground input of O2 by seagrasses, though not specifically indicated here does occur, and may be involved in sulfide oxidation (as in carbonate sediments) or in the oxidation of other reduced metabolites.
The study will utilize cutting-edge methods for evaluating oxygen and carbon exchange (Eulerian and eddy covariance techniques) combined with biomass, sedimentary, and water column measurements to develop and test numerical models that can be scaled up to quantify the dynamics of carbon cycling and sequestration in seagrass meadows in temperate and tropical environments of the West Atlantic continental margin that encompass both siliciclastic and carbonate sediments. The comparative analysis across latitudinal and geochemical gradients will address the relative contributions of different species and geochemical processes to better constrain the role of seagrass carbon sequestration to global biogeochemical cycles. Specifically the research will quantify: (i) the relationship between C stocks and standing biomass for different species with different life histories and structural complexity, (ii) the influence of above- and below-ground metabolism on carbon exchange, and (iii) the influence of sediment type (siliciclastic vs. carbonate) on Blue Carbon storage. Seagrass biomass, growth rates, carbon content and isotope composition (above- and below-ground), organic carbon deposition and export will be measured. Sedimentation rates and isotopic composition of PIC, POC, and iron sulfide precipitates, as well as porewater concentrations of dissolved sulfide, CO2, alkalinity and salinity will be determined in order to develop a bio-optical-geochemical model that will predict the impact of seagrass metabolism on sediment geochemical processes that control carbon cycling in shallow waters. Model predictions will be validated against direct measurements of DIC and O2 exchange in seagrass meadows, enabling the investigators to scale-up the density-dependent processes to predict the impacts of seagrass distribution and density on carbon cycling and sequestration across the submarine landscape.
Funding Agencies
The National Science Foundation funded this research.

Partners/Collaborators
This is a collaborative project with Richard Zimmerman and David Burdige from Old Dominion University.
