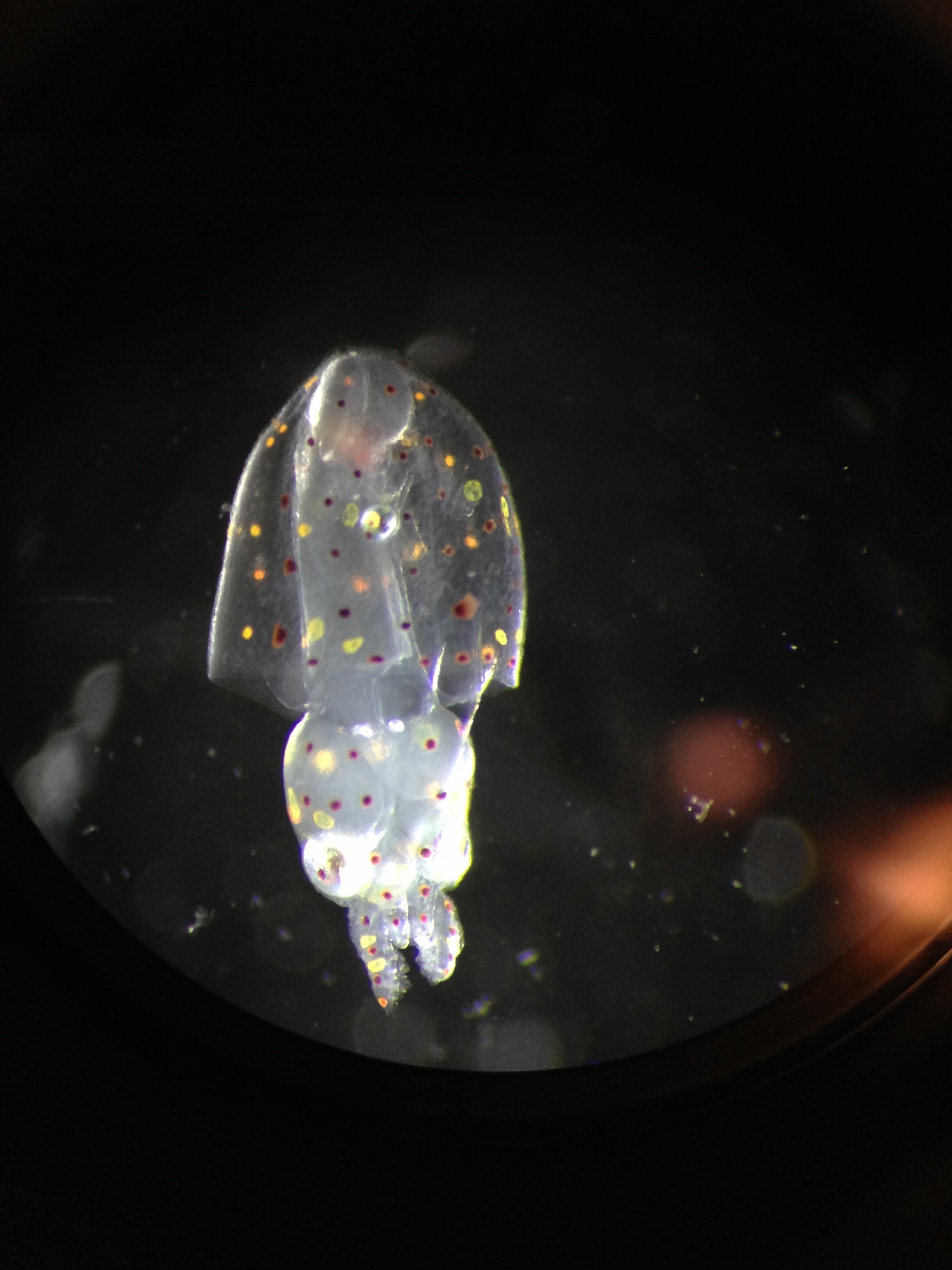
Squid Ocean Acidification
The goal of this work is to quantify how ocean acidification conditions impact squid (Loligo pealeii) embryo and paralarval development, behavior, and survival, as well as address the mechanisms that potentially induce these changes.
Cephalopods are critical components of many marine ecosystems. Squid in particular are often considered key species because of their central role in trophic webs, as the primary prey of numerous top predators, and the consumer of smaller meso- and epipelagic prey. While ocean acidification (OA) is poised to substantially impact a diverse array of marine organisms, there is little understanding of if or how decreasing pH and higher levels of CO2 may impact squid. Effects upon squid embryos and paralarvae may be of most concern because: (i) these developmental stages and their metabolism are highly sensitive to environmental conditions, (ii) they are initiating the construction of aragonite statoliths vital to orientation and sensory biology, and (iii) their successful early life history growth, behavior and survival are critical to founding future cohorts which support ecosystem food webs and global fisheries.
Our initial data indicate that high CO2 levels (2200 ppm) and low pH (7.4) induce changes in squid paralarval mantle length, development time, rate of hatching, statolith area, and statolith structure. Our current tests encompass current and predicted future CO2 levels (390-2200 ppm). We will hopefully produce effectual dose-response curves which are valuable for dynamic organisms which can occur in a range of environmental conditions. This upcoming work includes investigations of energy expenditures (via yolk sack size and swim velocity) and statolith mass and densities to address the potential mechanisms for changes in development, behavior and sensory physiology. Maintaining animals beyond hatching will allow estimates of survival potential. Final measurements will quantify the selectiveness of adults to lay eggs in the CO2 conditions in which effects were shown.