About Argo
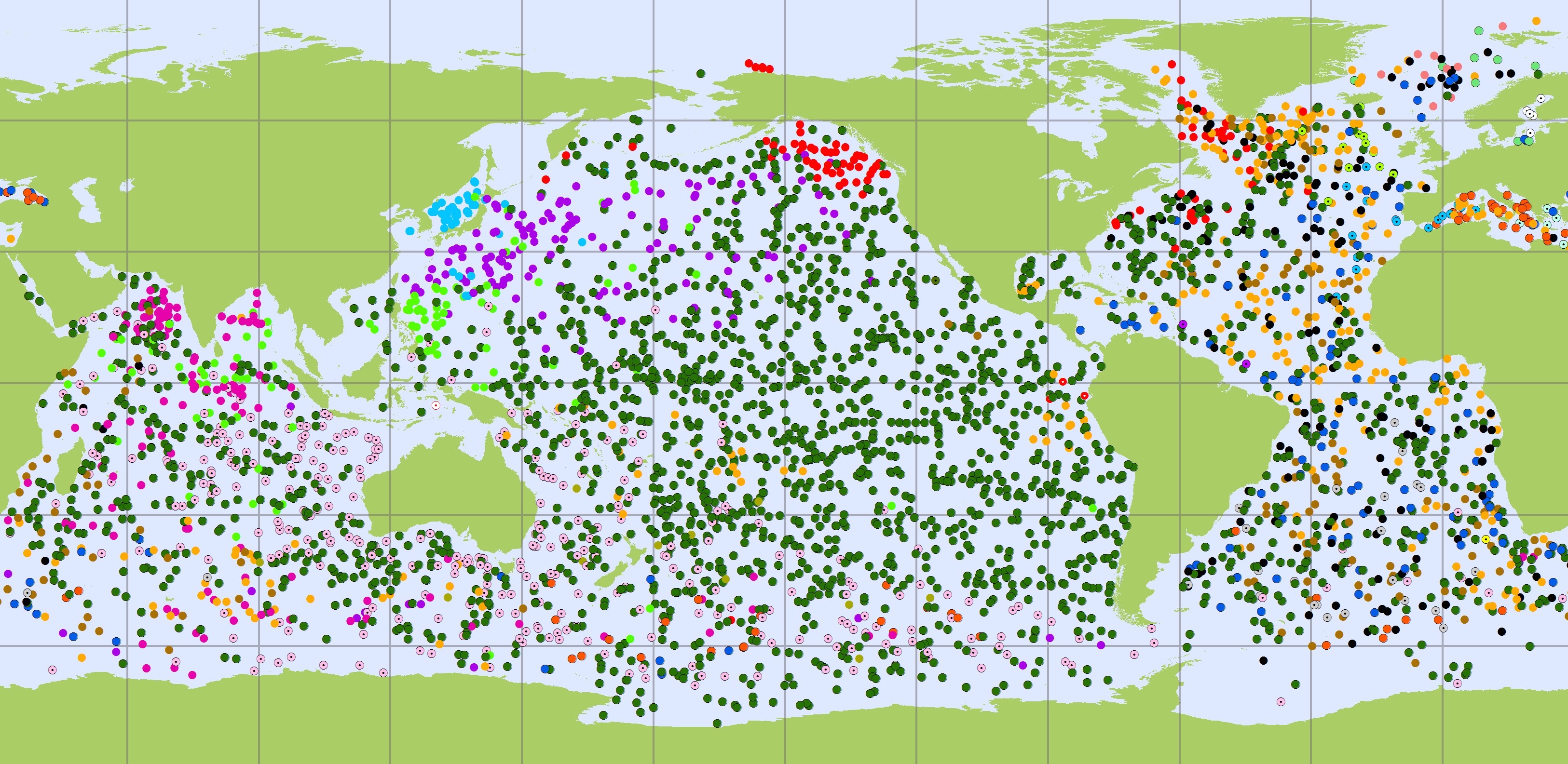
The Argo Program, launched in 1999, is a global array of floating robots that collect information about the physical state of the upper ocean, including temperature and salinity. Argo has passed its initial target of 3000 floats worldwide, with over 3900 floats currently taking measurements.
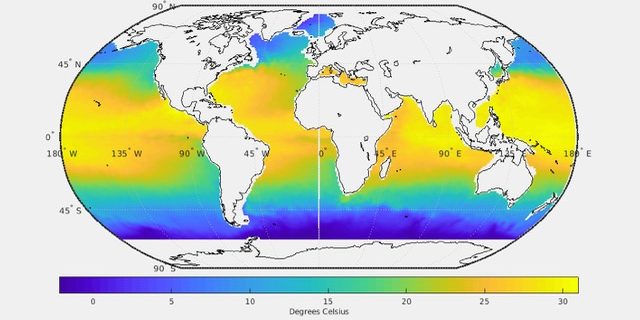
The basic goal of Argo is to track where heat and salinity are changing across the global ocean, down to a depth of 2000 meters. Argo sends that information to scientists and operational agencies in real time to assist ocean research and forecasting.
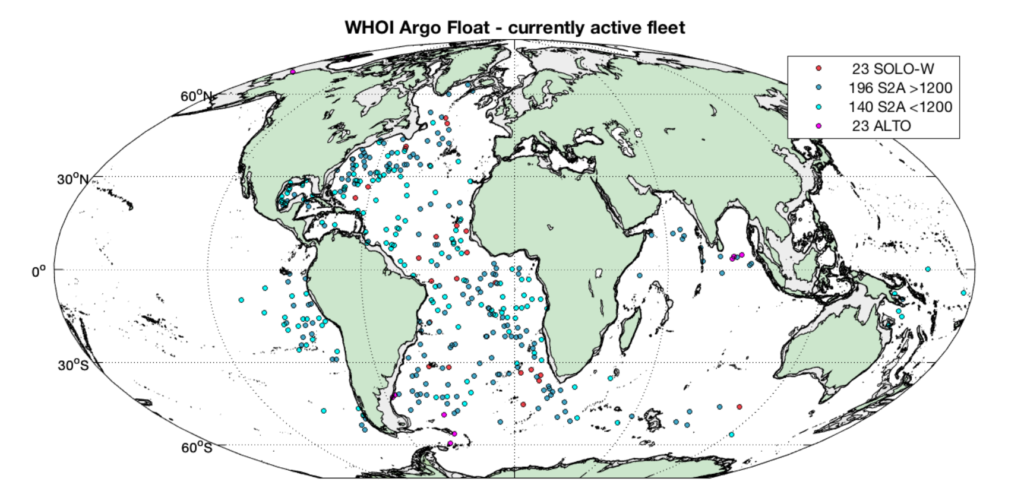
One of the original Argo member institutions, WHOI maintains about 10% of the global float array. The combined United States Argo program in turn operates 50% of the global array.
To learn about the international program, visit the Argo Steering Team website.
To learn more about the integrated, global effort for leveraging new technologies to expand the Argo program's data collection into the deep ocean, marginal seas, and biological and chemical realms, visit WHOI's OneArgo page.