Double-diffusive staircase
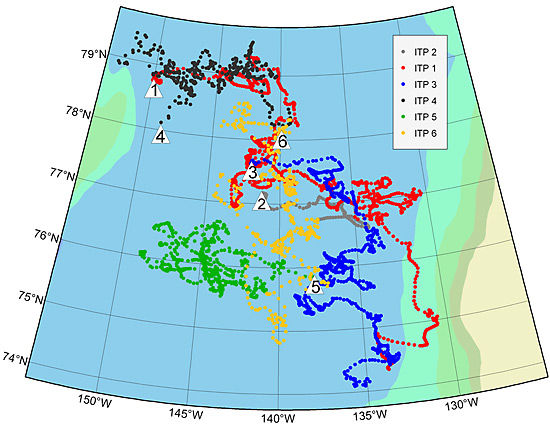
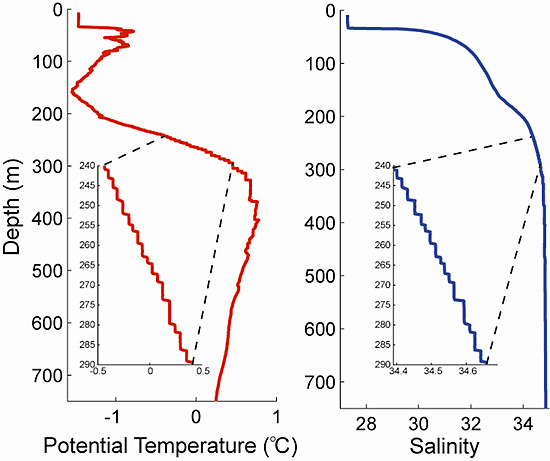
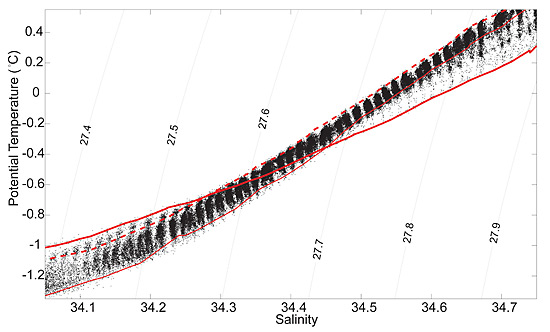
Six ITPs deployed in the central Canada Basin of the Arctic Ocean between 2004 and 2007, have provided detailed potential temperature and salinity measurements of a double-diffusive staircase at about 200-300-m depth (figures 1 and 2). Individual layers in the staircase are of order 1 m in vertical height but appear to extend horizontally for hundreds of kilometers, with along-layer gradients of temperature and salinity tightly bounded (figure 3).
Based on laboratory-derived double-diffusive flux laws, estimated vertical heat fluxes through the staircase are in the range 0.05 - 0.3 W/m2, only about 1/10 of the mean surface mixed-layer heat flux to the sea ice (figure 4). It is thus concluded that the vertical transport of heat from the Atlantic Water in the central basin is unlikely to have a significant impact to the Canada Basin ocean surface heat budget. Icebreaker CTD data from the Beaufort Gyre Freshwater Experiment show that the staircase is absent at the basin periphery. Turbulent mixing that presumably disrupts the staircase might drive greater flux from the Atlantic Water at the basin boundaries and possibly dominate the regionally-averaged heat flux.
Reference: Timmermans, M.-L., Toole, J., Krishfield, R. and Winsor, P. (2008) Ice-Tethered Profiler observations of the double-diffusive staircase in the Canada Basin thermocline. Journal of Geophysical Research, 113, C00A02, doi:10.1029/2008JC004829.