Evaporation and Precipitation
Evaporative and precipitative fluxes are defined with the sign convention that an upward directed flux is a positive quantity.
Evaporation and Sublimation
From a knowledge of the specific humidity (Gill, 1982) we compute the evaporation rate over the ocean surface as 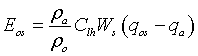 . This is in units of m/s and is evaluated at a sea water equivalent density.
. This is in units of m/s and is evaluated at a sea water equivalent density.
Analogously, we compute the sublimation rate over the ice/snow surface as 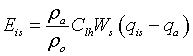 . This is in units of m/s and is evaluated at a sea water equivalent density.
. This is in units of m/s and is evaluated at a sea water equivalent density.
Precipitation - Regional Models
Regional AOMIP models will use a monthly precipitation climatology from Serreze and Hurst (2000) (download using link on sidebar). The data unit is mm/month expressed as a freshwater equivalent. The data format is explained below:
The data set on on an 89x89 array (7921 data points), which corresponds to 100 km grids. (a version of the NSIDC EASE grid). Values for latitudes below 60oN are given missing value codes (9999). Precip is in mm. There are 16 col:
1) grid # (1-7921)
2) lat
3) long
4-15) precip for Jan-Dec
16) Annual precip
The data represent interpolation of data from the Russian North Pole archive, coastal and inland stations. The Legates/Willmott climatology is used at a first guess, which is adjusted by the station data using a Cressman routine.
real zgrid,lat(89,89),long(89,89),precip(89,89,13)
do i=1,89
do j=1,89
read(1,*) zgrid,lat(i,j),long(i,j),(precip(i,j,m),m=1,13)
end do
end do
There is unfortunately no reference. Best to say that the data represents "an improved version of the climatology used by Serreze and Hurst [2000] that includes gauge-corrected monthly precipitation over the Arctic Ocean from the Russian North Pole drifting station and a larger set of coastal stations. The gauge corrections of the North Pole data are described by Yang [1999]"
Yang, D., 1999: An improved precipitation climatology for the Arctic Ocean, Geophys. Res. Lett., 26(11), 1625-1628.
The data represents an improved version of the climatology used by Serreze and Hurst (2000) that includes gauge-corrected monthly precipitation over the Arctic Ocean from the Russian North Pole drifting stations and a larger set of coastal stations. The gauge corrections of the North Pole data are described by Yang (1999).
Precipitation - Global Models
Global AOMIP models will use the monthly precipitation climatology from Xie-Arkin (1996, 1997) available to download using the link in the sidebar at the right side of the page. This data set will provide somewhat different precipitation forcing than that of the regional AOMIP models.